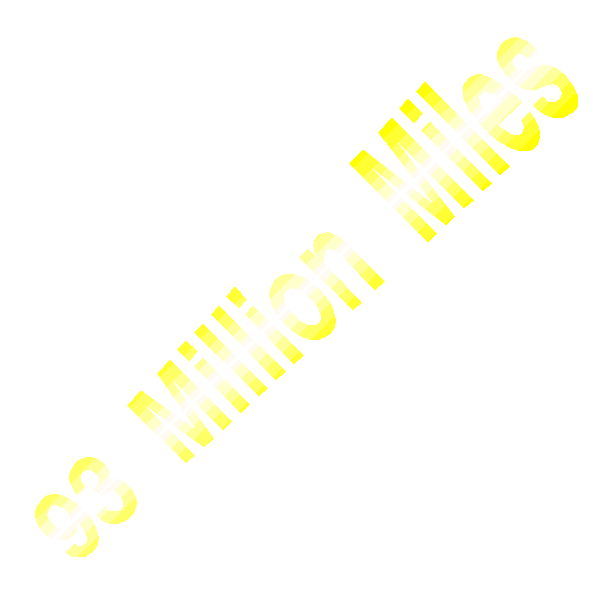Eco-Pros
Environmental Education on the Web
|
|
.gif)
GLOBAL WARMING
|
| Scientists around the world are trying to determine how
much of a role human activities are playing in causing rising
temperatures, the hole in the ozone layer, and major changes in climate
patterns - and how much of these changes are just part of the natural
processes that Earth has experienced over 4.5 billion years. The
changes seem to be occurring more rapidly than what we believe to be
natural processes, so it is believed that human activities are
responsible for the drastic changes in Earth's temperature causing global
warming. |
|
A delicate balance in nature
has evolved over billions of years
creating a livable and life-producing planet
|
|
The average temperature in the
center of the Sun is about 27,000,000°F, and the outer
"surface" is approximately 10,000°F.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Sun emitting
energy/radiation. |
|
The Sun's energy travels 93 million miles
at
the speed of light
(186,282 miles or 299,792 kilometers per second)
and reaches Earth in 8.4
minutes!
|
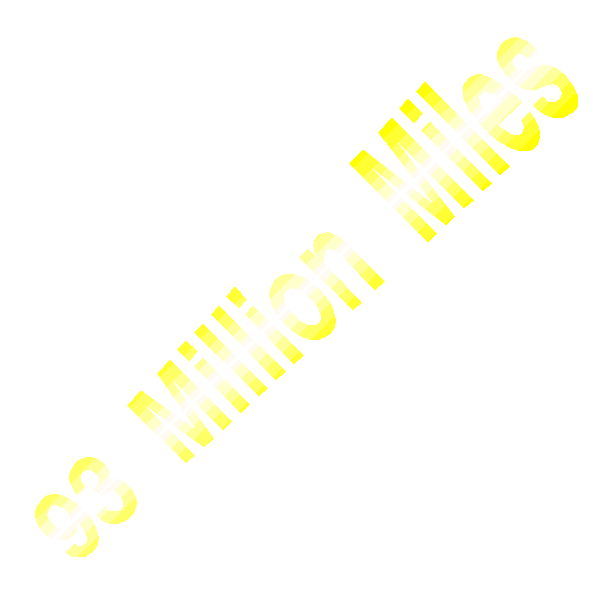
|
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE
Ozone in the stratosphere shields Earth from much harmful ultraviolet
(UV) radiation.
|
|
Solar energy arrives in
the form of short-wavelength radiation (high energy)
and enters Earth's upper
atmosphere with
the intensity of about
three
100-watt light bulbs per square yard (square yard = a square 3 ft. wide by 3
ft. long)
|
|
|
|
  
|
|
|
|
  |
|

|
Not all of this solar
energy is absorbed on Earth's surface.
1/3 of
the heat/energy is reflected back out into space,
in the form of long-wavelength, infrared radiation (low energy).
|
|
2/3 of the solar
energy/heat reaching Earth from the sun is trapped inside the
atmosphere by gases which absorb it. This is called the "greenhouse" effect.
|
 |
|
|

|
But, not all of the longwave radiation
escapes out into space, because .
the greenhouse gases absorb longwave radiation -
|
and again radiates it back down to the surface of the Earth causing additional warming.

Incoming shortwave radiation can pass through the gases in Earth's
atmosphere as it travels toward Earth, but longwave radiation
gets absorbed or trapped by greenhouse gases. This is similar to the
"heat-trapping" glass in a greenhouse, and thus is known as
the greenhouse effect..
|
| There is concern that as
concentrations of greenhouse gases increase, more heat is being
re-radiated back to Earth and increasing surface temperatures. |
|
SOLAR HEAT REFLECTED
Solar energy/heat can be reflected back into space from clouds, ice,
and snow; and human-related changes and activities, such as:
development, aerosols, pavement, smoke, sulfates. |
SOLAR HEAT ABSORBED AND
TRAPPED
Solar energy/heat is trapped and absorbed by water vapor, carbon dioxide and other gases in the
atmosphere. Gases which trap and retain solar heat in our atmosphere are called
"greenhouse gases."
"In order of abundance and importance as greenhouse gases are water vapor
(H20), carbon dioxide (CO2), ozone (O3), nitrous oxide
(N2O), methane (CH4), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)."
(GSFC/NASA). Some gases absorb and trap more heat per molecule than
others.
|
|
|

The greenhouse effect provides a blanket of warmth enveloping earth, which we need.
Otherwise we would freeze!
|
|
Without a natural greenhouse effect, the temperature of Earth would be
about zero degrees F (-18°C) instead of its present 57°F (14°C). (NCDC/NOAA)
|
|
And if the temperature of Earth was around zero degrees, what would
happen to our water supplies? The greenhouse effect is necessary
to maintain the liquid state of water in the Earth's biosphere.
So, we need the greenhouse effect, but things are getting a little too
warm.
|
|


.gif)